MiDoRe
Organisation
Maker's Asylum /
IDC SChool of Design
Industry
Year
1 week, Jan 2020
Role
Student designer
Background
🎥 WATCH THE VIDEO OR READ THROUGH
What was wrong?
When visually impaired people have to read staff notation, they have to run their fingers over the sheet, memorise the piece, and then play it on their instrument. This process is time-consuming and they are dependent on their memory.
Validating the problem
Methods used to validate the problem
Key findings
Initially, the problem statement was to design a melody music (western) instrument for visually impaired children of the age of 10-15 years, to assist them in learning music.
But after meeting the user we found that visually impaired musicians and learners are forced to read braille music, memorize a phrase and practice that, making it difficult and time-consuming for them.
brainstorming ideas
tech & Logistical challenges
We were working on a short project with Arduino, so we couldn't create solid plastic mockups. However, we used laser cut MDF to create prototypes.
How might we…
… offer a solution that would enable visually impaired musicians to haptically feel the notes, thereby saving their time and reducing their dependency on memory?
Ideation
method used to ideate
Goals of the workshop
Design a working wearable with available technologies (laser cutting & 3D printing) that would communicate staff notation through haptics
ideation at the workshop
experimenting
OUtcomes of the workshop
✔️We were able to create a few paper mockups and test out different placements, electronics and haptics
Designing
target persona
Prototyping
We made four paper prototypes for different placements to recognize the optimal area of sensitivity.
Different wearables wearable created for the arm, palm, wrist, and dorsal side. These prototypes were tested on different users before developing the final prototype.
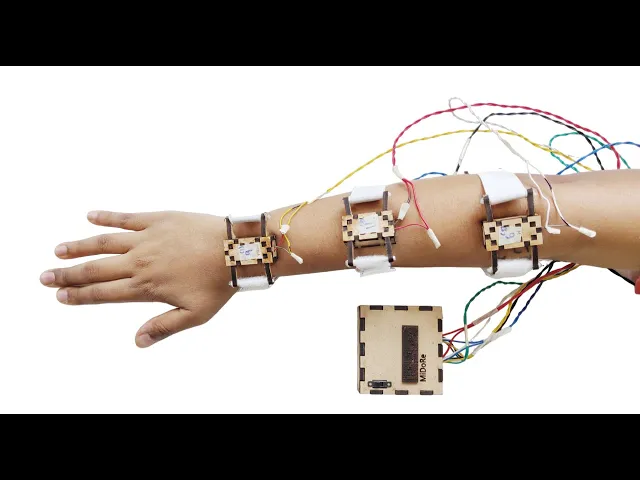
The musical notes are converted into braille notes and sent to six vibrating modules on this wearable mimicking the braille notation.
The wearable is placed on the user's arm were they get the braille notes in real time to play the instrument.
assembly
Final positions of the sensors
Final wearable: With 6 sensors and Arduino
Evaluation
method used to evaluate
Evaluating with participants
key findings
The most notable feedback was the size of the wearable was big and it should be closer to each other so that it can be easily recognized as a braille note.
Moreover, at some points, the vibrations spread which hindered the notes hence the placement of the wearable should be tested further for optimum results.
Sharps and flats in the music notes should be included in the notation. Moreover there could be more songs that can be converted, stored, and sent to the device.






